Effective Strategies for Treating Lumbar Strain and Backs
Dealing with lumbar strain and back pain can be both painful and disruptive to daily life. Whether caused by improper lifting, prolonged poor posture, or sudden movement, lumbar strain is one of the most common causes of back discomfort worldwide. Understanding effective strategies for treating lumbar strain not only alleviates pain but also helps prevent future episodes. In this article, we’ll explore the best approaches to manage lumbar strain and restore your back’s health and strength.
What is Lumbar Strain?
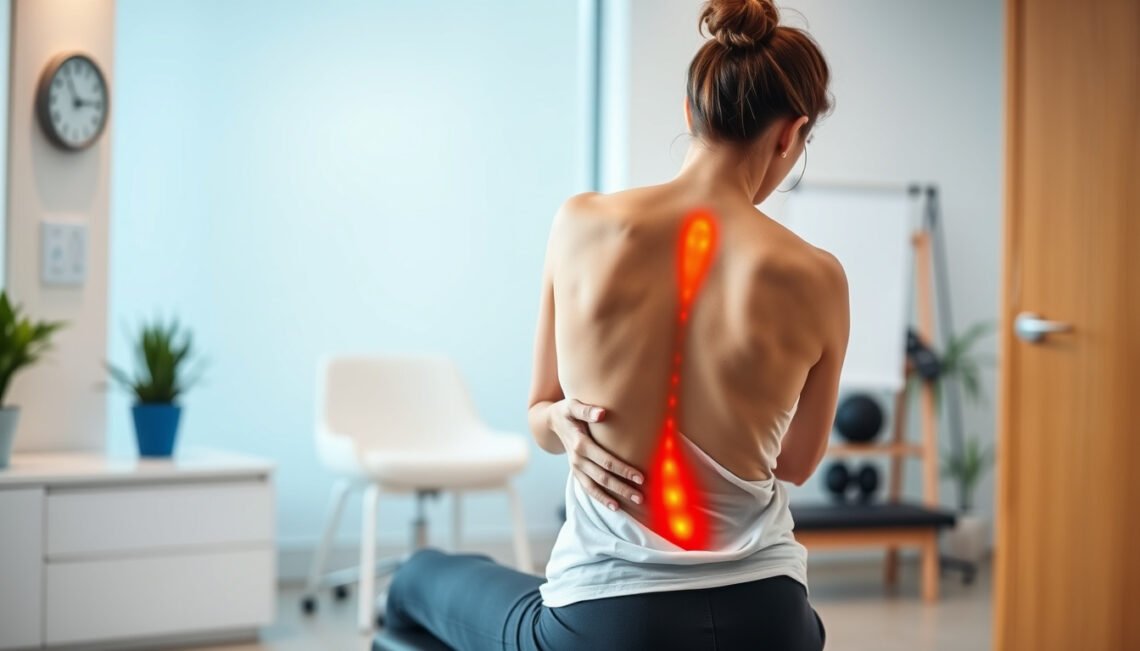
Lumbar strain refers to the overstretching or tearing of muscles, tendons, or ligaments in the lower back, specifically the lumbar region. This injury results in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, often developing suddenly or gradually over time. The lumbar spine’s complex structure—supporting vital organs and enabling movement—makes it particularly susceptible to strain from overexertion or poor biomechanics.
Understanding the nature of lumbar strain is essential for effective treatment. While it is usually not severe enough to cause nerve damage, untreated or poorly managed lumbar trauma can lead to chronic back issues.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Lumbar Strain
Early identification of lumbar strain symptoms can facilitate prompt treatment. Common signs include:
- Dull or sharp pain localized in the lower back
- Stiffness and difficulty moving or bending
- Muscle spasms in the lower back area
- Increased pain with movement or activity
- Relief with rest and minimal movement
If you experience severe pain, numbness, weakness in your legs, or loss of bladder or bowel control, seek immediate medical attention, as these could be signs of more serious conditions.
Effective Strategies for Treating Lumbar Strain
Managing lumbar strain involves a combination of self-care, physical therapy, and sometimes medical intervention. Below are authoritative strategies tailored to ease pain and promote recovery.
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is crucial initially to allow damaged muscles and tissues to recover. However, prolonged bed rest can weaken muscles, so balancing rest with gentle activity is essential. Limit activities that exacerbate pain, like heavy lifting or twisting. Gradually reintroduce movement to prevent stiffness and promote circulation.
2. Apply Cold and Heat Therapy
- Cold Therapy: Applying an ice pack during the first 48 hours after injury reduces inflammation and numbness of painful areas.
- Heat Therapy: After the initial inflammation subsides, heat pads or warm baths help relax muscles and improve blood flow.
3. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen are effective for reducing pain and inflammation associated with lumbar strain. Always follow dosing instructions and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
4. Gentle Stretching and Physical Therapy
Once acute pain subsides, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can restore flexibility and support the lower back. Physical therapy programs tailored to lumbar strain often include:
- Core strengthening
- Flexibility routines
- Posture correction
Top exercises to consider include:
- Pelvic tilts
- Cat-cow stretches
- Knee-to-chest stretches
5. Maintain Proper Posture and Ergonomics
Poor posture, especially during long sitting periods, can aggravate lumbar strain. Use ergonomic chairs with lumbar support, keep your feet flat on the ground, and maintain a neutral spine position when sitting or standing.
6. Lifestyle and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your lumbar spine, decreasing the risk of recurrent strain. Incorporate regular low-impact activities like walking or swimming to strengthen your back muscles.
7. When to See a Healthcare Professional
While many lumbar strain cases resolve with conservative treatment, persistent pain or worsening symptoms warrant professional evaluation. Your doctor may suggest imaging tests like MRI to rule out other causes and recommend advanced treatments such as physiotherapy, injections, or, rarely, surgery.
Preventing Lumbar Strain in Daily Life
Prevention plays a key role in avoiding recurring lumbar strain. Consider these proactive measures:
- Use proper lifting techniques: bend at your hips and knees, not your waist.
- Strengthen core muscles to support your spine.
- Maintain good posture during sitting, standing, and sleeping.
- Take frequent breaks during prolonged activities or desk work.
- Use supportive footwear and maintain an active lifestyle.
Summary of Effective Treatment Strategies for Lumbar Strain
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Rest & Activity Modification | Allow initial healing, avoid aggravating movements | Reduce further injury |
| Cold & Heat Therapy | Minimize inflammation, relax muscles | Manage pain effectively |
| OTC Pain Relievers | Alleviate discomfort | Ease symptoms |
| Physical Therapy & Exercise | Strengthen and stretch back muscles | Prevent future episodes |
| Posture & Ergonomics | Maintain spinal health | Reduce strain during daily tasks |
| Lifestyle Changes | Promote overall spinal health | Prevent recurrence |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How long does lumbar strain typically take to heal?
A: Most cases of lumbar strain improve within a few days to a few weeks with proper care. Severe cases may take longer, especially if not managed effectively.
Q2: Can I continue exercising if I have lumbar strain?
A: Gentle movements like walking and stretching are usually beneficial, but avoid high-impact or strenuous activities until pain subsides. Always consult a healthcare provider before resuming intense exercise.
Q3: What are some ways to prevent lumbar strain?
A: Proper lifting techniques, maintaining good posture, strengthening core muscles, and avoiding prolonged sitting or improper ergonomics can significantly help prevent lumbar strain.
Sources and Additional Resources
For more detailed information on managing back pain and lumbar strain, visit reputable sites like the Mayo Clinic (source). They provide comprehensive guidance on back injury prevention and treatment options.
Final Thoughts
Lumbar strain is a common, but manageable condition. By implementing effective treatment strategies—from proper rest and pain management to physical therapy and lifestyle modifications—you can facilitate recovery and minimize the likelihood of future episodes. Remember, early intervention and proactive prevention are key to maintaining a healthy, pain-free back. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice if your symptoms persist or worsen. Prioritize your spinal health today and take active steps toward a stronger, more resilient back!