Nerve root irritation is a common condition that can lead to significant discomfort, impacting one’s mobility and quality of life. Understanding nerve root irritation—its symptoms, underlying causes, and available treatment options—is essential for timely diagnosis and effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about nerve root irritation, aiming to empower readers with the knowledge to address this often painful condition.
What Is Nerve Root Irritation?
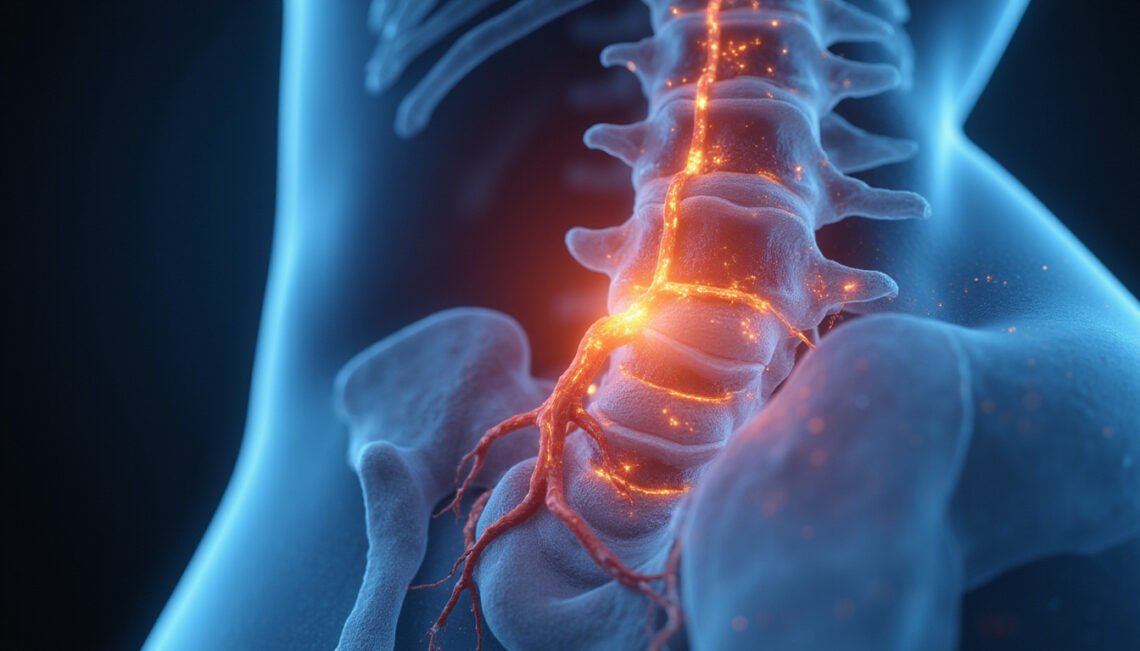
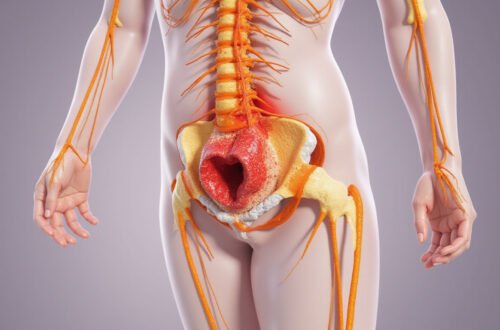
Nerve root irritation occurs when the nerve roots, which emerge from the spinal cord, become inflamed or compressed. These nerve roots are responsible for transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the rest of the body, enabling sensation and muscle control. When irritated, these nerve roots can cause pain, numbness, or weakness that typically radiates along the nerve’s path.
Common Symptoms of Nerve Root Irritation
Recognizing the symptoms of nerve root irritation is crucial to seeking medical evaluation and treatment promptly. Symptoms vary depending on which nerve root is affected but often include:
- Radiating pain: Sharp or burning pain that travels from the spine down the arms or legs.
- Numbness or tingling: Sensations likely experienced in the extremities served by the irritated nerve.
- Muscle weakness: Weakness in muscles controlled by the affected nerve roots may affect mobility and coordination.
- Reflex changes: Decreased reflexes in the limbs.
- Localized back or neck pain: Persistent pain near the affected spinal segment.
Symptoms often worsen with certain movements, like bending, twisting, or prolonged sitting or standing.
Common Causes of Nerve Root Irritation
Understanding the causes of nerve root irritation helps in targeting the right treatment and potentially preventing future episodes. Key causes include:
- Herniated Discs: Discs that slip or rupture can press against nerve roots, causing irritation.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal compresses nearby nerve roots.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Wear and tear on spinal discs can reduce cushioning, contributing to nerve compression.
- Bone Spurs: Overgrowths of bone can impinge nerve roots, often due to arthritis.
- Injury or Trauma: Accidents causing fractures or misalignment can irritate nerve roots.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like infections or autoimmune diseases may inflame the nerve roots.
Diagnostic Approaches for Nerve Root Irritation
To confirm nerve root irritation, healthcare professionals typically begin with a detailed history and physical examination. Diagnostic tools may include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The gold standard for visualizing soft tissues, discs, and nerves.
- CT Scans: Useful in viewing bone structures more clearly.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests assess electrical activity in muscles and nerves, indicating nerve root involvement.
Accurate diagnosis is vital for formulating an effective treatment plan.

Effective Treatment Options for Nerve Root Irritation
Treatment for nerve root irritation depends on severity, underlying cause, and patient-specific factors. Most cases improve significantly with conservative (non-surgical) care. Here are key treatment options:
1. Conservative Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce nerve pressure.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs reduce inflammation and alleviate pain; muscle relaxants or nerve pain medications may also be prescribed.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms helps reduce irritation.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat relaxes muscles while cold reduces swelling.
2. Interventional Treatments
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Corticosteroids injected near the irritated nerve root can reduce inflammation and provide lasting relief.
- Nerve Blocks: Temporary nerve blocks may diagnose and alleviate nerve pain.
3. Surgical Treatments
Surgery is generally reserved for patients who do not improve with conservative measures or have significant neurological deficits. Surgical options include:
- Discectomy: Removal of herniated disc portions compressing the nerve root.
- Foraminotomy: Enlarging the spinal canal opening to relieve nerve pressure.
- Spinal Fusion: Stabilizing the spine in cases of instability.
Lifestyle Changes for Preventing Nerve Root Irritation
Integrating healthy habits into daily life may reduce the risk of nerve root irritation:
- Maintain proper posture while sitting and standing.
- Incorporate regular low-impact exercise (e.g., walking, swimming).
- Use ergonomic furniture during work.
- Practice safe lifting techniques to avoid spinal injury.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the spine.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nerve Root Irritation
Q1: What is the difference between nerve root irritation and a pinched nerve?
A1: The terms are often used interchangeably; however, a pinched nerve generally refers to physical compression causing irritation of the nerve root. Nerve root irritation encompasses inflammation or other causes beyond mere compression.
Q2: Can nerve root irritation heal on its own?
A2: Mild cases of nerve root irritation may resolve with conservative self-care over weeks to months, especially with rest and physical therapy. Persistent or severe cases typically require medical intervention.
Q3: What exercises are best for nerve root irritation?
A3: Exercises focusing on spinal stabilization, gentle stretching, and strengthening of core muscles are beneficial. It’s important to perform these under professional guidance to avoid further irritation.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms of nerve root irritation—including persistent radiating pain, numbness, or weakness—do not improve with rest or worsen, seeking medical evaluation promptly is critical. Early treatment can prevent chronic pain and neurological damage.
The comprehensive management of nerve root irritation involves understanding its symptoms, causes, and the array of treatment options available. By taking proactive steps including physical therapy, medication, and, in some cases, surgery, many individuals regain function and reduce pain effectively.
For more detailed information about spinal conditions and nerve root irritation, you can visit resources such as the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) which offers expert insights and treatment advice (source).
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms suggestive of nerve root irritation, do not delay in consulting a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment can make a profound difference in recovery outcomes. Take control of your spinal health today!