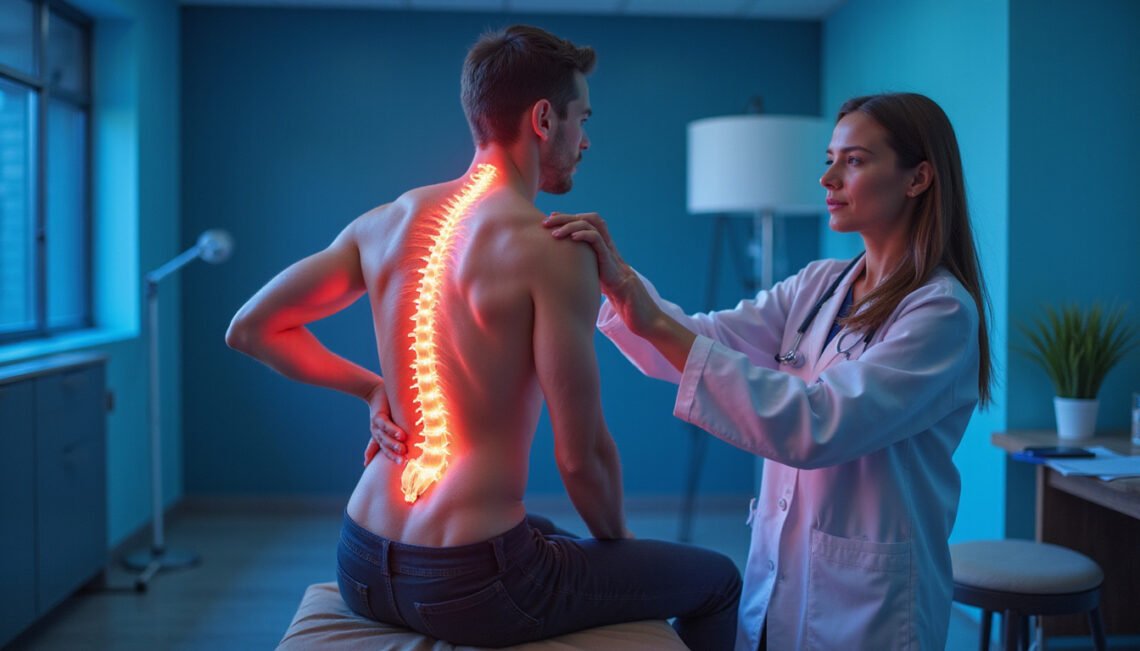
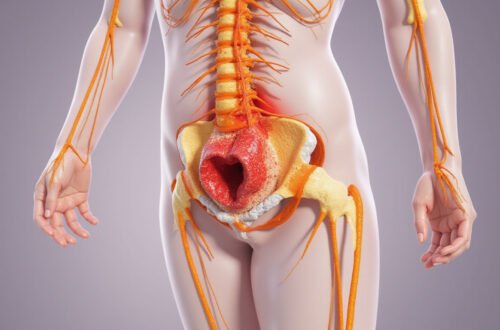
Sciatica diagnosis plays a crucial role in effectively managing and alleviating the painful symptoms associated with sciatica. Sciatica is characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. Understanding the steps involved in sciatica diagnosis not only helps in identifying the root cause of the pain but also guides appropriate treatment options for relief and recovery.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the signs and symptoms to watch for, the diagnostic procedures commonly used, and effective treatments following an accurate sciatica diagnosis.
Understanding Sciatica and the Importance of Diagnosis
Sciatica is not a disease itself but a symptom of an underlying medical condition, most often caused by irritation, inflammation, pinching, or compression of the sciatic nerve. Common causes include herniated disks, spinal stenosis, or piriformis syndrome. Because the sciatic nerve affects various regions of the lower body, symptoms can vary widely, making accurate sciatica diagnosis essential.
Without proper diagnosis, sciatica symptoms might be misattributed to other conditions like muscle strain or hip problems, delaying crucial treatment. Early and precise identification helps prevent worsening of symptoms, improves pain management, and can even prevent permanent nerve damage.
Common Symptoms Indicating Sciatica
Recognizing the symptoms that warrant a sciatica diagnosis is the first step towards effective treatment. The hallmark signs include:
- Sharp, shooting pain radiating from the lower back, through the buttock, and down the back of one leg
- Numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness in the affected leg or foot
- Pain worsening with sitting, standing for long periods, or sudden movements
- Difficulty moving or controlling the leg due to pain or weakness
- A burning or electric shock sensation along the nerve pathway
If these symptoms persist beyond a few days or worsen, seeking medical evaluation for a sciatica diagnosis is advisable.
Key Steps in Sciatica Diagnosis
Healthcare providers rely on a combination of patient history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests to confirm sciatica and understand its underlying cause.
1. Initial Medical History and Symptom Review
The process usually begins with a detailed medical history where the healthcare provider asks about:
- The location, intensity, and pattern of the pain
- Activities or positions that worsen or relieve the symptoms
- Any history of injury or trauma to the spine or pelvis
- Previous treatments tried and their effectiveness
This contextual information helps narrow down possible causes of sciatica.
2. Physical Examination
During the physical exam, physicians assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation in the legs and feet. Tests may include:
- Straight Leg Raise Test: The patient lies on their back while the provider lifts the extended leg; pain during this maneuver often suggests sciatic nerve irritation.
- Motor and Sensory Testing: Helps determine if there is weakness or numbness corresponding to specific nerve roots.
3. Imaging and Diagnostic Tests
In cases where symptoms are severe, persistent, or accompanied by neurological deficits, imaging is crucial for sciatica diagnosis. Common modalities include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The gold standard for visualizing nerve compression, herniated discs, and other structural problems in the spine (source).
- CT Scan or CT Myelogram: Alternative options for patients unable to undergo MRI.
- X-rays: Used to detect fractures or degenerative spinal conditions but less detailed for nerve issues.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity of muscles and nerves to evaluate nerve damage.
Once a sciatica diagnosis is established, treatment can be tailored to the severity and specific cause of the symptoms. A multidisciplinary approach often yields the best results.

Treatment Approaches Following Sciatica Diagnosis
1. Conservative Treatments
Most people with sciatica respond well to non-surgical treatments, including:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercise programs improve flexibility, strengthen muscles supporting the spine, and reduce nerve pressure.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and in some cases, oral steroids or neuropathic pain medications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding prolonged sitting, practicing good posture, and ergonomic adjustments.
2. Interventional Therapies
For persistent or severe cases:
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Help reduce inflammation around the irritated nerve.
- Nerve Blocks: Can provide temporary relief in specific nerve-related pain.
3. Surgical Options
When conservative methods fail, or there is significant nerve impairment, surgery may be considered to relieve compression. Procedures include:
- Microdiscectomy for herniated disc removal
- Laminectomy to widen the spinal canal
Tips to Prevent Sciatica Recurrence
After successful treatment following sciatica diagnosis, prevention is key to avoid future episodes:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce spine stress.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercise such as walking or swimming.
- Practice proper lifting techniques to avoid injury.
- Use ergonomic furniture and support during prolonged sitting.
FAQ About Sciatica Diagnosis
Q1: How long does it take to get a sciatica diagnosis after symptoms start?
A: Many healthcare providers can initially diagnose sciatica based on symptoms and physical exam within a single visit. Additional imaging might require days or weeks depending on availability.
Q2: Can sciatica diagnosis be done at home?
A: While some self-assessment tools exist, a definitive sciatica diagnosis requires a professional evaluation including physical exams and often imaging.
Q3: What tests confirm sciatica diagnosis?
A: MRI is the preferred imaging test to confirm sciatica, especially to identify nerve compression or disc herniation, along with clinical assessment.
Conclusion: Take Action Today for Effective Sciatica Diagnosis and Relief
Accurate sciatica diagnosis is the foundation of effective treatment and lasting relief. If you experience persistent pain radiating down your leg, numbness, or weakness, don’t ignore these warning signs. Early consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to targeted diagnostic testing and prompt treatments that improve your quality of life.
By understanding the key steps in sciatica diagnosis and engaging in proactive treatment, you can significantly reduce pain, restore mobility, and prevent further complications. Take the first step today—schedule a medical evaluation if you suspect sciatica symptoms. Your path to recovery begins with the right diagnosis.