Radiculopathy is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. If you’ve been experiencing sharp pain, numbness, or weakness radiating from your spine into your arms or legs, you might be dealing with radiculopathy. Understanding radiculopathy symptoms and treatments is crucial for managing the condition effectively and improving your quality of life. This article explores what radiculopathy is, its key symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and practical advice for anyone affected by it.
What Is Radiculopathy?
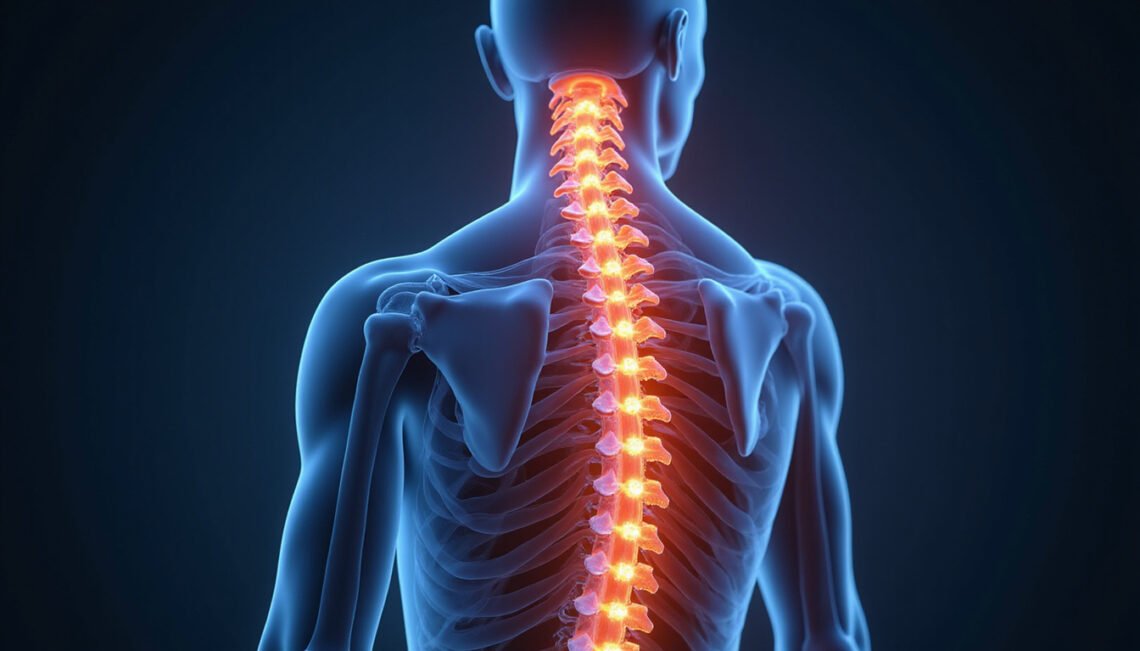
Radiculopathy refers to the irritation, inflammation, or compression of a nerve root as it exits the spinal column. This condition can occur in various parts of the spine: cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), or lumbar (lower back). The outcome is nerve dysfunction, which results in pain, tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness along the nerve’s pathway.
The most common cause of radiculopathy is a herniated disc pressing on the nerve roots, but other causes include spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal), bone spurs, or injury. Because the symptoms are linked directly to the affected nerve root, radiculopathy can significantly impact your mobility and daily activities if left untreated.
Recognizing Radiculopathy Symptoms
Identifying radiculopathy symptoms early can make a big difference in treatment success. Symptoms usually develop gradually but can sometimes be sudden, particularly after an injury.
Common symptoms of radiculopathy include:
- Radiating pain: Sharp or burning pain that radiates from the spine to the arms or legs, depending on the affected region.
- Numbness or tingling: A “pins and needles” sensation often experienced in the arms, hands, legs, or feet.
- Muscle weakness: Difficulty moving or controlling muscles supplied by the affected nerve, impacting grip strength or walking.
- Loss of reflexes: Decreased or absent tendon reflexes in the affected limb.
- Sensory changes: Altered sensation or reduced ability to feel heat, cold, or touch.
The location of symptoms correlates with the spinal level affected. For example, cervical radiculopathy affects the neck, shoulders, and arms, whereas lumbar radiculopathy affects the lower back, buttocks, and legs.

Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the root causes and risk factors helps in the prevention and management of radiculopathy. Some common causes include:
- Herniated discs: When the soft gel inside the disc bulges out and presses on nearby nerves.
- Degenerative disc disease: Age-related wear and tear that causes discs to lose height and become less flexible.
- Spinal stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal creates pressure on nerve roots.
- Bone spurs: Extra bone growth that can impinge on nerves.
- Injury or trauma: Sudden impact or accidents causing nerve root damage.
- Diabetes: Can lead to nerve damage over time.
- Poor posture and repetitive movements: Prolonged poor ergonomics and repetitive stress increase risk.
How Is Radiculopathy Diagnosed?
A proper diagnosis of radiculopathy involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and imaging tests.
- Medical history and symptom review: Your doctor will ask about the distribution of pain, duration, associated symptoms (e.g., weakness, numbness), and potential injury history.
- Physical exam: This focuses on neurological assessment, including muscle strength, reflex testing, sensory evaluation, and specific maneuvers like the straight-leg raise test for lumbar nerve irritation.
- Imaging studies: Tools such as MRI, CT scans, or X-rays help visualize the spine structures and identify compression or abnormalities affecting nerve roots.
- Electrodiagnostic tests: Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) may be used to assess nerve function and confirm radiculopathy.
Effective Treatments for Radiculopathy
The treatment approach for radiculopathy depends on symptom severity, underlying cause, and duration. Most cases respond well to conservative treatments, while more severe or persistent symptoms might require surgical intervention.
Conservative Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Specialized exercises improve flexibility, strength, and posture, alleviating nerve pressure.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) help reduce inflammation and pain. In some cases, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants, corticosteroids, or neuropathic pain medication.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms and using ergonomic supports can help.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying cold packs reduces inflammation, while heat relaxes muscles and improves blood flow.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: For more severe symptoms, targeted injections reduce nerve inflammation directly.
Surgical Options
Surgery may be necessary if conservative treatments fail or if there is significant nerve compression causing muscle weakness or loss of function. Common surgical procedures include:
- Discectomy: Removal of herniated disc material that is pressing on the nerve.
- Laminectomy: Removal of part of the vertebra (lamina) to relieve pressure.
- Foraminotomy: Widening the passage where the nerve exits the spinal canal.
According to the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS), surgery often leads to rapid pain relief and improved nerve function for appropriate candidates (source).
Tips for Living with Radiculopathy
Managing radiculopathy isn’t solely about medical treatment — lifestyle modifications play a critical role in recovery and preventing recurrence. Here are practical tips for coping with radiculopathy:
- Maintain good posture: Use ergonomic chairs and correct spine alignment during sitting and standing.
- Stay active but avoid overexertion: Gentle exercises and walking improve circulation and strength without worsening symptoms.
- Use supportive devices: Braces or cushions can help stabilize the spine during flare-ups.
- Apply heat and cold appropriately: Use ice packs for acute pain and heat for muscle relaxation.
- Monitor symptoms: Keep a pain diary and report new or worsening symptoms promptly to your healthcare provider.
Bulleted Summary of Radiculopathy Symptoms and Treatments
- Symptoms:
- Radiating pain in arms or legs
- Numbness and tingling sensations
- Muscle weakness and loss of reflexes
- Sensory changes in affected limbs
- Causes: Herniated discs, spinal stenosis, bone spurs, injury, diabetes
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, imaging (MRI, CT), EMG/NCS tests
- Conservative treatments: Physical therapy, medication, activity modification, steroid injections
- Surgical options: Discectomy, laminectomy, foraminotomy
- Lifestyle tips: Good posture, regular gentle activity, supportive devices
FAQ About Radiculopathy
Q1: How long does radiculopathy last?
The duration of radiculopathy varies but many cases resolve within a few weeks to months with conservative treatment. Chronic radiculopathy may require more intensive management.
Q2: Can radiculopathy heal on its own?
Yes, mild radiculopathy can often improve without surgery as inflammation decreases and the nerve recovers, especially with physical therapy and activity modifications.
Q3: What is the difference between radiculopathy and sciatica?
Sciatica is a type of radiculopathy specifically caused by compression of the sciatic nerve roots in the lumbar spine, resulting in radiating pain down the leg.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Nerve Health Today
Radiculopathy symptoms can be painful and disruptive, but early diagnosis and treatment make a significant difference in outcomes. Whether you are experiencing mild tingling or debilitating weakness, understanding the condition empowers you to take control and seek proper care. Consult your healthcare provider about your symptoms, explore tailored treatment options, and adopt healthy lifestyle changes to support your spine and nerve health.
Don’t let radiculopathy hold you back — start your journey to pain relief and improved mobility today! For personalized guidance and the latest treatment innovations, speak to a spinal specialist and take the first step toward a healthier, more comfortable life.