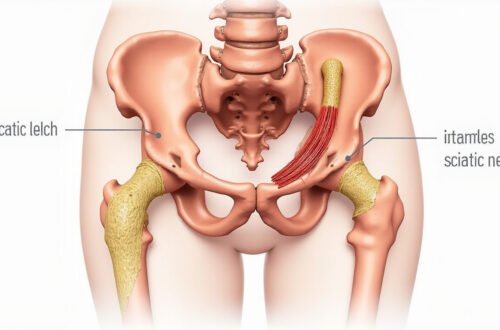
Lumbar radiculopathy is a condition that can significantly impact your daily life, causing discomfort and limiting your mobility.
Whether you’re experiencing persistent pain, numbness, or weakness in your back and legs, understanding this condition is the first step towards finding relief.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects of lumbar radiculopathy, including its symptoms, causes, diagnostic methods, and a range of effective treatment options to help you reclaim your health and well-being.
Your Sciatica Pain-Free Future Starts Here – Click to Learn More!
Key Takeaways
- Lumbar radiculopathy is a condition caused by nerve compression in the lower back, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness.
- Common symptoms include sharp shooting pain in the leg, tingling sensations, and difficulty in movement.
- Understanding the risk factors such as age, obesity, and occupation can help in identifying potential cases of lumbar radiculopathy.
- Diagnostic methods like MRI and EMG play a crucial role in confirming the presence of lumbar radiculopathy.
- Effective treatment options range from physical therapy to surgical interventions, and preventive lifestyle adjustments are key to managing the condition.
What is Lumbar Radiculopathy?
Lumbar radiculopathy is a medical condition that occurs when one or more of the nerve roots in the lower back become pinched or irritated, often leading to pain, numbness, or weakness that radiates down the leg.
This condition typically results from issues such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease, which can put pressure on the spinal nerves.
Individuals experiencing lumbar radiculopathy might describe symptoms ranging from sharp, shooting pain to tingling sensations in the lower extremities, impacting their daily activities and overall quality of life.
It’s crucial for anyone facing these symptoms to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies, which may include physical therapy, medication, or in some cases, surgical intervention to relieve the pressure on the affected nerves.
Common Symptoms of Lumbar Radiculopathy
Lumbar radiculopathy is a condition characterized by pain and discomfort that arises from the compression or irritation of the spinal nerves in the lower back, and recognizing its common symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
Individuals experiencing lumbar radiculopathy often report sharp or burning pain that radiates down the leg, typically following the path of the affected nerve.
This pain may be accompanied by numbness, tingling sensations, or weakness in the lower extremities, which can significantly impact daily activities.
Many people may also experience difficulty standing up straight or bending due to increased pain during certain movements.
In some cases, the symptoms might vary in intensity and could exacerbate when sitting for long periods or during specific physical activities.
Understanding these symptoms is essential, as early recognition can lead to more effective treatment options and better management of the condition.
‘Pain is inevitable. Suffering is optional.’ – Haruki Murakami
Causes and Risk Factors
Lumbar radiculopathy, often referred to as sciatica, occurs when a nerve in the lower back becomes compressed or irritated, leading to a variety of symptoms that can impact daily life.
Several causes contribute to this condition, with herniated discs being one of the most common culprits, as they can bulge out and press against nearby nerve roots.
Other factors include spinal stenosis, where the spinal canal narrows over time, and degenerative disc disease, which involves the gradual wear and tear of the disks cushioning the spine.
Risk factors for developing lumbar radiculopathy include age, as wear on the spine increases with time, and lifestyle factors such as obesity and sedentary habits, which can put excess strain on the lower back.
Additionally, occupations that require heavy lifting or repetitive bending may elevate the risk, as can certain sports and physical activities that improperly load the spine.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and for seeking timely treatment to alleviate discomfort and avoid further complications.
Your Sciatica Pain-Free Future Starts Here – Click to Learn More!
Diagnostic Methods for Lumbar Radiculopathy
When it comes to diagnosing lumbar radiculopathy, a condition often characterized by pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower back and legs caused by nerve compression, healthcare professionals utilize a variety of diagnostic methods to confirm the condition and assess its severity.
Initially, a thorough medical history and physical examination play a crucial role, allowing the physician to evaluate the patient’s symptoms and functionality.
Following this, imaging techniques such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scans are commonly employed to visualize the spine and identify any herniated discs or bony stenosis that may be pressing on the nerve roots.
Additionally, nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) may be utilized to evaluate nerve function and muscle response, providing further insight into the extent of nerve involvement.
By integrating these diagnostic approaches, clinicians can formulate an accurate diagnosis of lumbar radiculopathy and develop a tailored treatment plan that best addresses the individual’s needs.
Treatment Options for Lumbar Radiculopathy
When it comes to treating lumbar radiculopathy, it’s essential to approach the condition with a multifaceted strategy tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Conservative treatments often start with physical therapy, where targeted exercises and stretching can help alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and manage discomfort.
For some patients, epidural steroid injections can provide significant relief by directly targeting inflamed nerve roots.
In cases where conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief, surgical options—such as microdiscectomy or spinal fusion—may be considered to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
It’s crucial to engage in a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider to understand the benefits and risks of each treatment option and to create a personalized plan that encourages recovery and enhances quality of life.
FAQs
What is lumbar radiculopathy?
Lumbar radiculopathy is a condition that occurs when the nerves in the lower back are compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness that can radiate down the legs.
What are the common symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy?
Common symptoms include sharp or burning pain in the lower back, pain that radiates down the legs, numbness or tingling in the legs or feet, and muscle weakness in the affected areas.
What causes lumbar radiculopathy?
Lumbar radiculopathy can be caused by various factors such as herniated discs, bone spurs, spinal stenosis, or injury.
Risk factors include age, obesity, and occupations involving heavy lifting.
How is lumbar radiculopathy diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and nerve conduction studies to assess nerve function.
What treatment options are available for lumbar radiculopathy?
Treatment options may include physical therapy, medication like anti-inflammatories or corticosteroids, epidural steroid injections, and in some cases, surgical procedures to relieve nerve pressure.