Herniated discs can be a source of discomfort and confusion for many. In this article, we will delve into what a herniated disc actually is, explore the common causes and symptoms, and discuss effective treatment options available. Whether you’re experiencing back pain or simply seeking to understand this condition better, our comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights. Let’s embark on this journey to demystify herniated discs and learn how to manage and prevent them.
Your Sciatica Pain-Free Future Starts Here – Click to Learn More!
Key Takeaways:
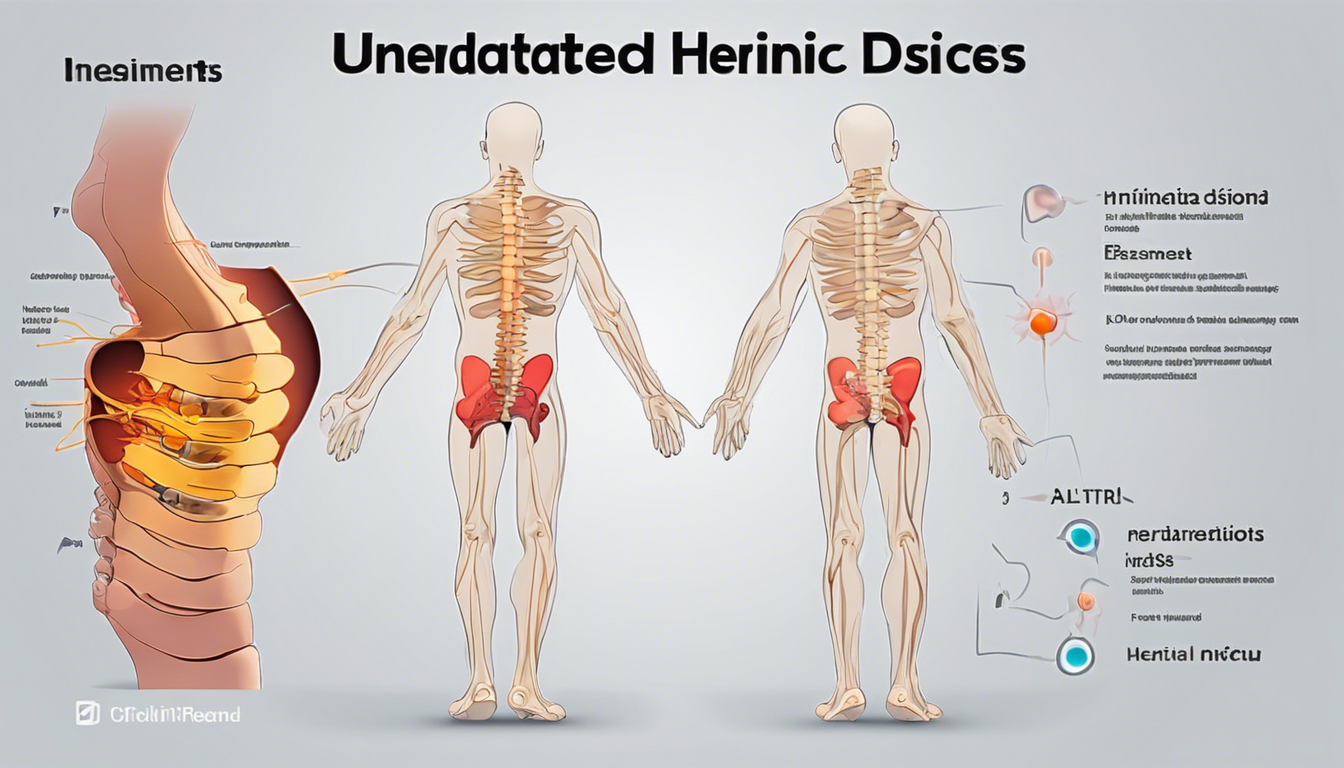
- A herniated disc occurs when the soft material inside a disc bulges out, potentially pressing on nerves.
- Common causes of herniated discs include age, obesity, and heavy lifting.
- Key symptoms of a herniated disc can include pain, numbness, and weakness in affected areas.
- Diagnosis typically involves physical examinations and imaging techniques like MRIs or CT scans.
- Effective treatments range from physical therapy to surgery, with lifestyle changes helping to prevent future issues.
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, often referred to as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when one of the rubbery cushions (discs) located between the vertebrae in your spine becomes damaged and bulges or breaks open. This can lead to pressure on nearby nerves, resulting in symptoms such as pain, numbness, or weakness, particularly in the back, neck, arms, or legs, depending on the location of the herniation. While some may experience mild discomfort, others may find their daily activities severely affected. Factors such as age, genetics, and lifestyle choices like improper lifting or sitting for extended periods can contribute to their development. Understanding a herniated disc is crucial, not just for recognizing potential symptoms but also for seeking appropriate treatment options to alleviate discomfort and promote recovery.
Common Causes of Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner gel of a spinal disc protrudes through a tear in the tougher exterior casing, often leading to discomfort and pain. This condition is commonly caused by a variety of factors, starting with age-related degeneration, which can weaken the discs over time, making them more susceptible to injury. Heavy lifting or an abrupt twist can also contribute to the development of a herniated disc, as these actions place excessive pressure on the spine. Additionally, sedentary lifestyles and poor posture—especially when sitting for prolonged periods—can lead to increased stress on spinal structures, increasing the risk. Other underlying factors, such as obesity or genetic predisposition, may further elevate the chances of experiencing this painful condition. Understanding these common causes can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their spinal health.
‘The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall.’ – Nelson Mandela
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
Recognizing the symptoms of a herniated disc is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Individuals may experience a variety of signs that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, typically beginning with localized back pain that can radiate to other areas, such as the legs or arms. In many cases, people report sensations like numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected limb, which can interfere with daily activities. Additionally, you might notice difficulties in your ability to stand or sit comfortably for prolonged periods. While these symptoms can mimic those of other conditions, being aware of them can help you seek appropriate medical attention. If the pain persists or worsens, or if you experience bowel or bladder issues, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional, as these can signal severe complications. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve the outlook and help you return to your routine with minimal limitations.
Your Sciatica Pain-Free Future Starts Here – Click to Learn More!
Diagnosis and Imaging Techniques for Herniated Discs
Diagnosing a herniated disc typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination conducted by a healthcare professional. During the physical exam, the doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, such as pain, numbness, or weakness, which can indicate nerve involvement. To confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions, imaging techniques are crucial. The most commonly used methods include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which provides detailed images of the spinal structures and can highlight the extent of the disc herniation, and Computed Tomography (CT) scans, which might be used if an MRI is contraindicated. X-rays can also be employed, though they are less effective for visualizing soft tissue structures like discs. In some cases, advanced imaging techniques such as myelography, which involves injecting contrast dye into the spinal canal, may be recommended. Understanding these diagnostic tools is essential, as they guide effective treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Effective Treatment Options for Herniated Discs
When facing the discomfort of a herniated disc, it’s essential to explore effective treatment options that cater to your specific needs. A herniated disc occurs when the inner gel-like material of a spinal disc bulges out, potentially compressing nearby nerves and leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs. Conservative treatments generally start with physical therapy, which can help strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility, thus alleviating pressure on affected nerves. In conjunction with physical therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers, or prescription medications, may be prescribed to manage inflammation and pain effectively. For those who do not respond to these initial therapies, spinal injections of corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief. In severe cases, surgical options like a discectomy or spinal fusion may be considered to remove the herniated portion or stabilize the spine, respectively. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the severity of the condition while aiming for a return to daily activities.