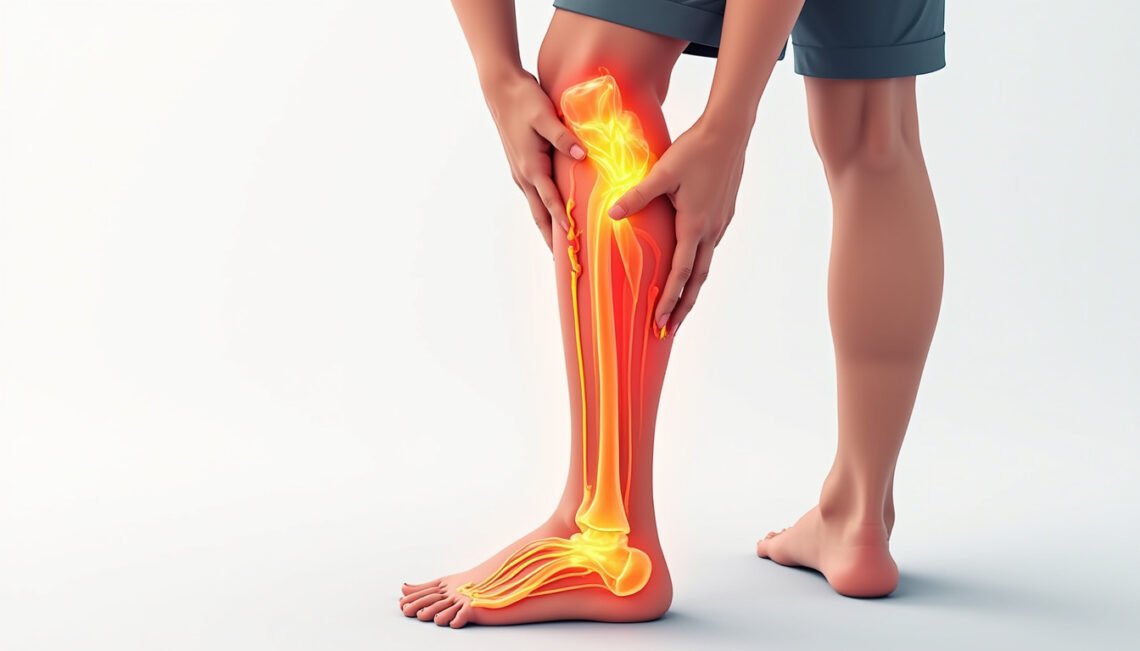
Sciatic neuropathy is a condition that affects the sciatic nerve, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness along the nerve’s pathway. This condition can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life if left untreated. Understanding sciatic neuropathy is crucial for recognizing its symptoms early and exploring effective treatments that can alleviate pain and improve nerve function.
In this article, we will explore the common symptoms and causes of sciatic neuropathy, discuss diagnostic approaches, and highlight treatment options that offer relief. Whether you’ve recently been diagnosed or are experiencing unexplained leg or back pain, this guide will provide valuable insights into managing sciatic neuropathy effectively.
What Is Sciatic Neuropathy?
Sciatic neuropathy refers to a disorder that damages or irritates the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the body. Originating from the lower spine, this nerve runs through the buttocks and down each leg. When the nerve is compromised, it causes pain, tingling, or weakness along its distribution, typically affecting one side of the body.
Unlike sciatica, which is a general term for symptoms caused by irritation of the sciatic nerve, sciatic neuropathy specifically implies nerve injury or dysfunction detectable by nerve conduction studies.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sciatic Neuropathy
Symptoms of sciatic neuropathy can vary depending on the severity and location of the nerve injury. Early recognition is essential for timely intervention.
Common symptoms include:
- Sharp or burning pain radiating from the lower back or buttock down the leg
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the thigh, leg, or foot
- Muscle weakness in the leg or foot, sometimes causing difficulty walking or standing
- Reduced reflexes at the knee or ankle
- Sensitivity to touch or decreased sensation in the affected areas
If you experience persistent leg pain accompanied by numbness or weakness, consulting a healthcare provider is vital to rule out sciatic neuropathy.
Causes of Sciatic Neuropathy
Understanding what causes sciatic neuropathy is key to preventing further nerve damage and tailoring appropriate treatment strategies.
Common causes include:
- Trauma or injury: Direct injury to the lower back or buttocks can compress or damage the sciatic nerve.
- Herniated lumbar disc: A common cause where a slipped disc in the lower spine presses on the nerve roots.
- Piriformis syndrome: When the piriformis muscle irritates or compresses the sciatic nerve.
- Nerve entrapment: Nerve compression due to tumors, cysts, or anatomical abnormalities.
- Diabetic neuropathy: High blood sugar levels leading to nerve damage.
- Infections or inflammatory conditions: Such as shingles or autoimmune disorders impacting nerve health.
- Surgical complications: Procedures involving the lower spine or hip area may inadvertently injure the nerve.
Diagnosing Sciatic Neuropathy
Diagnosis usually begins with a clinical evaluation focused on symptom history and physical examination. Tests may include:
- Neurological exam: Checking muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory function.
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies: To assess the electrical activity of muscles and the speed of nerve signals.
- Imaging studies: MRI or CT scans can identify structural causes like herniated discs or tumors.
- Blood tests: To detect underlying conditions such as diabetes or infections.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to distinguishing sciatic neuropathy from other causes of leg pain and identifying the most effective treatment.

Effective Treatments for Sciatic Neuropathy
Treatment plans should be individualized, depending on the cause and severity of the neuropathy. Below are common approaches:
1. Conservative Treatments
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and relieve nerve compression.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, or nerve pain medications like gabapentin.
- Activity modification: Avoiding movements that exacerbate symptoms and maintaining a healthy posture.
- Heat or cold therapy: Helps reduce inflammation and ease muscle spasms.
2. Advanced Therapies
- Epidural steroid injections: To reduce inflammation around the nerve.
- Nerve blocks: Local anesthetics to provide symptom relief.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture and chiropractic treatment have shown benefits for some patients.
3. Surgical Options
Surgery may be necessary when conservative treatments fail or if there is significant nerve compression causing muscle weakness or loss of function. Procedures include:
- Discectomy: Removal of herniated disc material.
- Decompression surgery: To relieve pressure on the nerve.
- Tumor removal: If a mass is causing sciatic nerve impairment.
Surgical outcomes often depend on the condition’s duration before intervention.
Preventing Sciatic Neuropathy
While some causes of sciatic neuropathy are unavoidable, certain lifestyle changes may reduce risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce spinal stress.
- Practice good posture and ergonomics.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercise such as walking or swimming.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or standing; take regular breaks to move.
- Manage underlying conditions like diabetes effectively.
When to Seek Medical Help
Seek prompt medical advice if you experience:
- Severe or worsening leg pain unresponsive to over-the-counter painkillers
- Muscle weakness or difficulty moving the leg or foot
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (a medical emergency)
- Numbness in the groin or inner thigh region
Early treatment can prevent permanent nerve damage and significantly improve outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Sciatic Neuropathy
Q1: How is sciatic neuropathy different from sciatica?
Sciatic neuropathy involves actual nerve damage or dysfunction proven by tests, whereas sciatica is a symptom characterized by pain along the sciatic nerve pathway without necessarily confirmed nerve injury.
Q2: Can sciatic neuropathy heal on its own?
In some mild cases, sciatic neuropathy may improve with rest, physical therapy, and medication. However, persistent or severe symptoms require medical intervention to prevent permanent nerve damage.
Q3: What types of doctors treat sciatic neuropathy?
Neurologists, orthopedic surgeons, pain specialists, and physical therapists often collaborate to diagnose and treat sciatic neuropathy effectively.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Sciatic Neuropathy Today
Sciatic neuropathy may cause distressing symptoms, but understanding its causes and treatments empowers you to take charge of your health. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive approach to management can dramatically reduce pain and restore mobility. If you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of sciatic neuropathy, don’t delay consulting a healthcare professional. With appropriate care—ranging from physical therapy to advanced interventions—you can regain your quality of life.
To start your journey toward recovery, schedule a consultation with a specialist and explore tailored treatment options. Remember, relief is possible, and proactive care is the key to overcoming sciatic neuropathy.
For more detailed information on sciatic nerve disorders and treatment, visit the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (source).