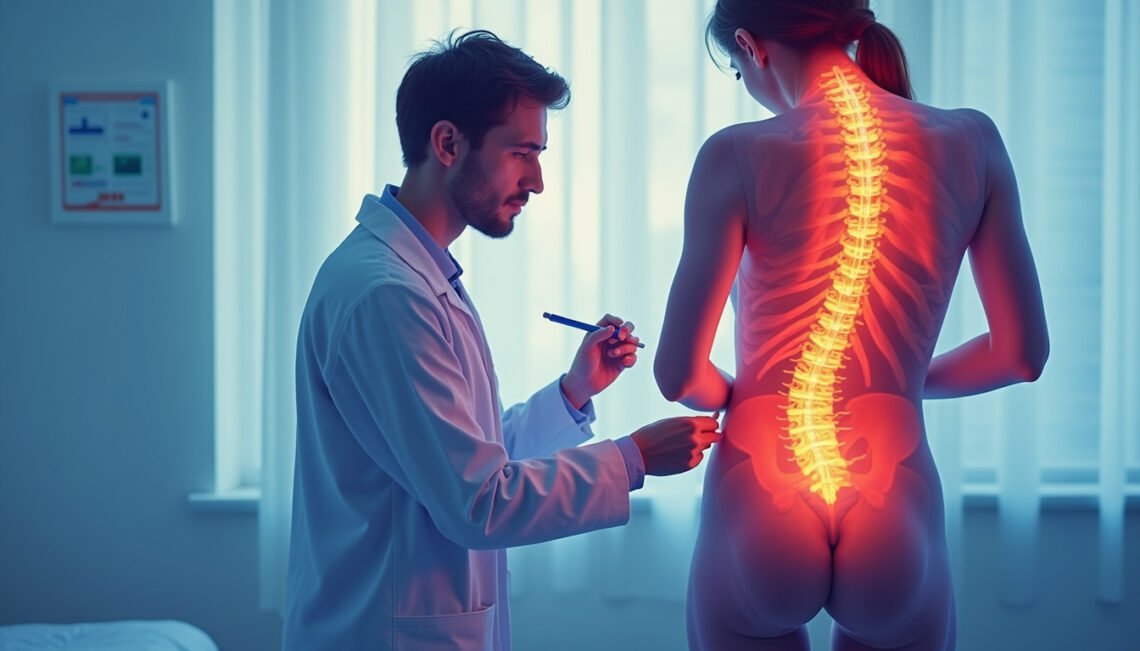
Sciatica diagnosis is a crucial step toward managing and relieving the severe pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, typically from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. Prompt identification and treatment of sciatica can prevent chronic discomfort and improve mobility, making it essential to understand the signs, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options.
In this article, we will explore the essential steps for an accurate sciatica diagnosis and provide guidance on how to treat this condition quickly and effectively.
Understanding Sciatica and Its Symptoms
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve—the longest nerve in the body—is compressed or irritated. This condition is often caused by a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or a bone spur pressing on the nerve. Knowing the symptoms associated with sciatica diagnosis can help individuals seek timely medical attention.
Common Symptoms of Sciatica:
- Sharp or burning pain radiating from the lower back to the thighs, calves, or feet
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the leg or foot
- Muscle weakness in the affected leg
- Difficulty moving or controlling the leg due to pain
- Pain worsening with prolonged sitting or sudden movements
Recognizing these symptoms early is the first step toward obtaining an accurate sciatica diagnosis and starting appropriate treatment.
The Initial Evaluation: When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent lower back pain radiating to the leg or toes, especially with associated numbness or weakness, it’s important to schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider. Early medical evaluation helps differentiate sciatica from other possible conditions such as peripheral neuropathy or vascular diseases.
During your first visit, your doctor will review your medical history, discuss your symptoms, and conduct a physical examination to evaluate muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation.
Diagnostic Procedures for Accurate Sciatica Diagnosis
An accurate sciatica diagnosis relies on both clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider may recommend the following:
1. Physical Examination
The doctor will perform specific maneuvers, such as the straight leg raise test, to check for nerve irritation. This involves raising the leg while keeping the knee straight to see if pain worsens.
2. Imaging Studies
Imaging tests can reveal structural causes of nerve compression:
- X-rays to identify bone abnormalities
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to view soft tissues like discs and nerves
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans to get detailed cross-sectional images
MRI is often the preferred tool as it provides clear information about herniated discs or spinal stenosis (source).

3. Electromyography (EMG)
This test measures electrical activity in muscles and nerves to detect nerve damage, helping confirm the site and severity of the compression.
Treatment Options Following Sciatica Diagnosis
Once sciatica diagnosis is confirmed, treatment can begin based on the severity and underlying cause. The primary goals are to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore function.
Conservative Treatments
Most people respond well to non-surgical treatments including:
- Physical therapy: Customized exercises to improve flexibility and strengthen back muscles
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription anti-inflammatory drugs
- Hot and cold therapy: Applying heat or ice packs to reduce pain and inflammation
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding prolonged sitting, practicing good posture, and incorporating ergonomic adjustments at work
Minimally Invasive Procedures
If pain persists despite conservative measures, your doctor may recommend:
- Epidural steroid injections to reduce inflammation around the nerve
- Nerve block injections for targeted pain relief
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is typically reserved for patients with severe sciatica symptoms unresponsive to other treatments or with progressive neurological deficits. Procedures such as microdiscectomy or laminectomy aim to remove the source of nerve compression and provide lasting relief.
Five Key Steps to a Timely Sciatica Diagnosis and Treatment
To effectively manage sciatica, follow these five essential steps:
- Recognize symptoms early: Monitor for radiating leg pain, numbness, and weakness
- Consult a healthcare professional promptly: Early evaluation avoids complications
- Undergo thorough diagnostic tests: Imaging and nerve studies confirm diagnosis
- Follow prescribed treatment plans: Adherence speeds recovery and prevents recurrence
- Incorporate preventive measures: Maintain spinal health with regular exercise and ergonomics
Frequently Asked Questions About Sciatica Diagnosis
Q1: How long does it take to get a sciatica diagnosis?
A1: Typically, diagnosis can be made during a physical exam and symptom review, often confirmed with imaging in a few days to weeks depending on access to tests.
Q2: Can sciatica diagnosis be done without an MRI?
A2: Yes, initial diagnosis may rely on physical exam and X-rays, but MRI provides more detailed information about nerve compression, which is often necessary for precise treatment planning.
Q3: Is sciatica diagnosis always accurate on the first visit?
A3: While many cases are identified early, additional tests or specialist referrals might be required if symptoms are unclear or if initial treatments fail.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Sciatica Today
Early and accurate sciatica diagnosis is the foundation of successful treatment and long-term relief. By paying attention to symptoms, seeking prompt medical care, and following recommended diagnostic and treatment steps, you can reduce pain quickly and improve your quality of life.
Don’t let sciatica control your daily activities—take action now. Contact a qualified healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms and begin the path to recovery. With the right diagnosis and treatment strategies, you can regain mobility, reduce pain, and prevent future episodes of sciatica.