Sciatica diagnosis is essential for anyone experiencing sharp pain radiating from the lower back down through the legs. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the diagnostic process can help provide relief and prevent long-term complications. This article discusses the key symptoms associated with sciatica, the tests doctors use for an accurate sciatica diagnosis, and the various treatment options available to manage this often debilitating condition.
Understanding Sciatica: What Is It?
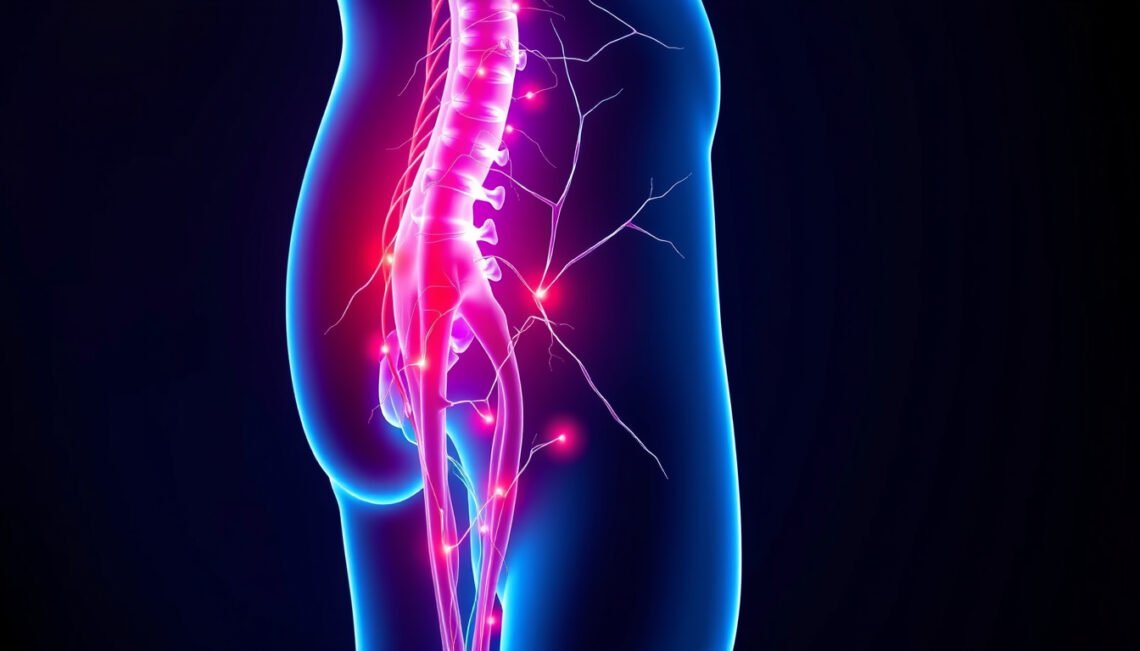
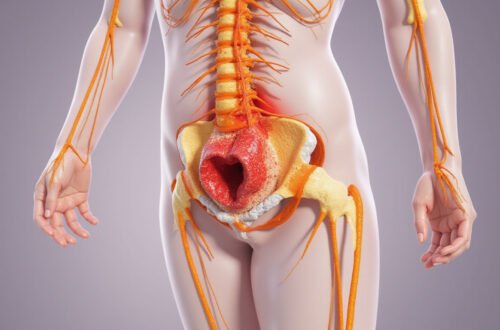
Before diving deep into sciatica diagnosis, it’s crucial to understand what sciatica actually is. Sciatica is a term used to describe pain that follows the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from your lower back, through the hips and buttocks, and down each leg. This nerve can become irritated or compressed, leading to various symptoms.
The sciatica diagnosis generally involves identifying the root cause of nerve irritation or compression, which can result from herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other spinal issues.
Key Symptoms of Sciatica
Recognizing the key symptoms is the first step in sciatica diagnosis. The most commonly reported complaints include:
- Radiating Pain: Pain that starts in the lower back or buttock and travels down one leg, often described as sharp, burning, or shooting.
- Numbness and Tingling: Patients may experience “pins and needles” sensations or numbness along the path of the sciatic nerve.
- Muscle Weakness: Depending on nerve involvement, weakness in the affected leg or foot may occur.
- Worsening With Movement: Sciatica pain often intensifies when sitting, coughing, sneezing, or moving.
- One-Sided Symptoms: Typically, sciatica affects only one side of the body.
Although the intensity can vary, persistent sciatica symptoms lasting more than a week should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional for proper sciatica diagnosis.
How Is Sciatica Diagnosed? Key Tests and Procedures
A thorough sciatica diagnosis involves several steps, starting with a detailed medical history and physical exam, followed by diagnostic testing if needed.
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor will first ask about the onset, duration, and character of your pain. They will check for muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation in your legs, which helps localize nerve involvement.
2. Straight Leg Raise Test
One common physical test is the straight leg raise, where the doctor lifts your leg while lying down. Pain radiating down the leg during this maneuver often indicates nerve root irritation associated with sciatica.
3. Imaging Tests
If the diagnosis remains uncertain or the symptoms are severe or persistent, imaging tests may be ordered:
- X-rays: Help rule out fractures, bone spurs, or spinal alignment problems.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The gold standard for visualizing soft tissues like discs, nerves, and spinal cord to identify herniated discs or nerve impingement.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Can be used when MRI is contraindicated or unavailable.
- Electrodiagnostic Tests (EMG/NCS): Measure nerve and muscle electrical activity to assess nerve function and location of damage.
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, MRI is most effective in confirming a sciatica diagnosis caused by herniated discs (source).

Treatment Options for Sciatica
Treatment for sciatica depends on the severity of symptoms and underlying causes. Most cases improve with conservative measures, but some require more intensive interventions.
Conservative Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Customized exercises improve flexibility, strengthen back muscles, and reduce nerve pressure.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as NSAIDs may reduce inflammation. In some cases, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants or stronger pain medications.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or ice packs can relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Activity Modification: Avoid prolonged sitting and perform gentle stretching to alleviate symptoms.
Interventional Treatments
If conservative treatments fail, options include:
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections near the affected nerve may reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
- Nerve Blocks: Used to pinpoint and alleviate nerve pain.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is generally reserved for severe cases, such as significant weakness or loss of bladder/bowel control, or when symptoms persist beyond six weeks despite other treatments. Common surgical procedures include:
- Microdiscectomy: Removal of the herniated disc portion pressing on the nerve.
- Laminectomy: Removal of bone or tissue compressing the nerve.
Top 5 Tips to Aid Recovery After Sciatica Diagnosis
- Stay Active: Gentle movement and walking help prevent stiffness.
- Follow a Physical Therapy Plan: Consistency enhances recovery.
- Maintain Good Posture: Reduces spinal strain.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: Avoids additional nerve stress.
- Listen to Your Body: Rest when needed but avoid prolonged inactivity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sciatica Diagnosis
Q1: How soon should I see a doctor after experiencing sciatica symptoms?
A: If pain lasts more than a week, worsens, or is associated with muscle weakness or loss of bladder/bowel control, see a healthcare provider immediately for sciatica diagnosis.
Q2: Is imaging always necessary to diagnose sciatica?
A: Not always. Initial diagnosis focuses on symptoms and physical exam. Imaging is used if symptoms persist or worsen to identify the exact cause.
Q3: Can sciatica diagnosis be made at home?
A: While you can recognize symptoms, a professional sciatica diagnosis requires clinical evaluation and possibly imaging or nerve tests.
Final Thoughts: Act Early for Effective Sciatica Management
Sciatica diagnosis is the crucial first step in managing this painful condition effectively. By recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate testing, patients can benefit from targeted treatments that reduce pain and improve function. Remember, conservative treatments often provide relief, but persistent or severe cases warrant professional evaluation.
Don’t let sciatica pain control your life. If you’re experiencing symptoms suggestive of sciatica, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough sciatica diagnosis and individualized treatment plan. Taking action early can help you reclaim mobility and enjoy pain-free days ahead!