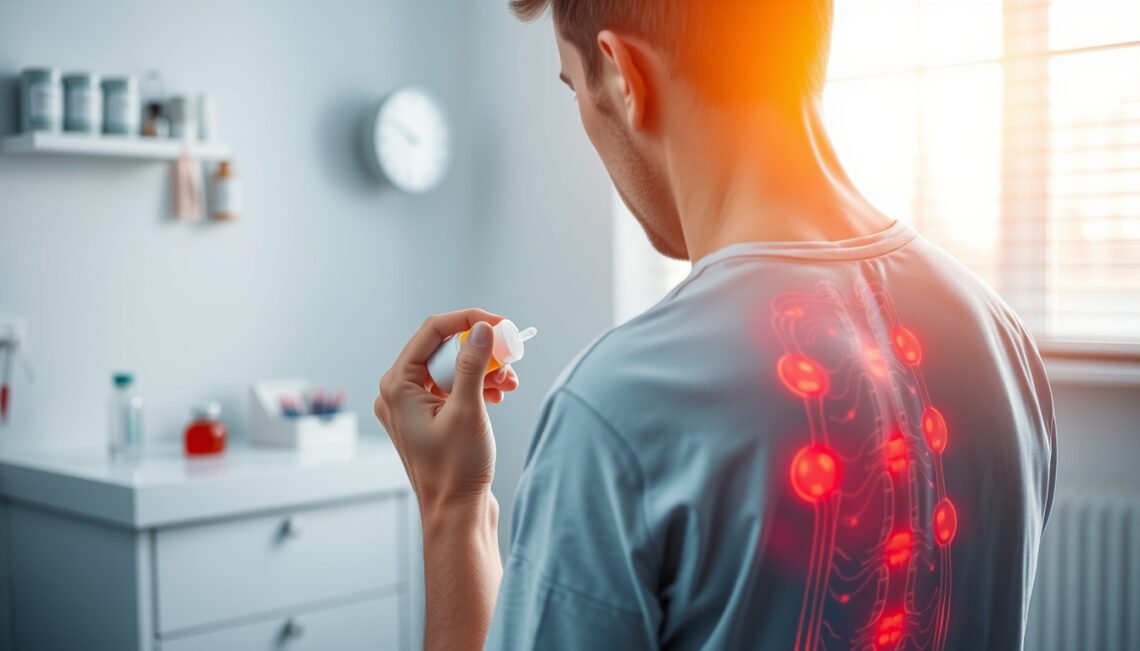
Sciatica is a common condition characterized by pain radiating along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from your lower back down through your hips and legs. Whether caused by a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or other nerve compression issues, managing sciatica pain promptly and effectively is essential for restoring daily comfort and mobility. One of the most sought-after approaches involves the use of specific sciatica medication. In this article, we’ll explore various medication options designed to alleviate sciatica pain quickly, helping you get back to your normal activities.
Understanding Sciatica and Its Treatment Goals
Before diving into medication options, it’s important to understand what causes sciatica and what treatments aim to achieve. Sciatica pain varies in intensity, from a dull ache to sharp, shooting pain that can be debilitating. The primary goals of treatment are to reduce inflammation, relieve nerve pressure, and control pain to improve quality of life.
While physical therapy and lifestyle modifications play roles in comprehensive management, medication is often a first-line treatment to manage acute symptoms effectively.
Common Types of Sciatica Medication to Relieve Pain Quickly
When seeking sciatica medication that offers quick relief, several options are available, each working through different mechanisms. Here are some of the most effective classes:
1. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are often the first choice for sciatica medication due to their anti-inflammatory properties, which help reduce nerve inflammation and pain.
Common NSAIDs include:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Aleve)
- Aspirin
How they work: These drugs inhibit enzymes involved in the inflammatory process, easing pain and swelling.
Considerations: NSAIDs can cause stomach irritation, so they should be taken with food and under medical supervision, especially for long-term use.
2. Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
While not an anti-inflammatory, acetaminophen is effective for pain relief and can serve as an alternative for those who cannot tolerate NSAIDs.
How it works: It acts centrally in the brain to modify the perception of pain.
Limitations: Not suitable for long-term chronic pain relief in severe cases but helpful for mild to moderate pain.
3. Muscle Relaxants
Sciatica can sometimes cause muscle spasms in the back or legs. Short-term use of muscle relaxants can relieve these spasms and associated pain.
Common muscle relaxants include:
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Methocarbamol
- Carisoprodol
How they work: They act on the central nervous system to reduce muscle spasm and discomfort.
Caution: Prolonged use may cause drowsiness and dependency; use only under medical guidance.
4. Prescription Oral Steroids
In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce nerve swelling and pain.
Examples include:
- Prednisone
- Methylprednisolone
Administration: Often given in short courses or oral tapering schedules.
Benefits: Can lead to rapid pain relief, especially when combined with physical therapy.
5. Neuropathic Pain Medications
Since sciatica involves nerve pain, certain medications targeting nerve signaling can provide relief.
Options include:
- Gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Pregabalin (Lyrica)
Mode of action: They modulate nerve signals to reduce nerve-related pain sensations.
Note: These medications may take a few days to weeks to reach full effectiveness but are vital for persistent nerve pain.
6. Topical Analgesics
For localized pain relief, topical treatments are increasingly popular.
Examples include:
- Capsaicin cream
- Lidocaine patches
Advantages: Minimal systemic side effects and targeted relief.
Combining Medications for Optimal Relief
Often, a combination of medications yields the best results, especially in severe cases. For instance, NSAIDs can be paired with muscle relaxants or neuropathic pain medications to address different pain pathways simultaneously. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment plans.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions Complementing Medication
While medication plays a crucial role, combining it with physical therapy, hot/cold therapy, and ergonomic adjustments can accelerate recovery and reduce reliance on drugs.
Safety Considerations When Using Sciatica Medication
- Follow dosing instructions carefully.
- Report any side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort or dizziness.
- Be aware of interactions with other medications.
- Avoid alcohol while on NSAIDs or steroids.
- Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or changing medication regimens.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sciatica Medication
1. What is the best sciatica medication for quick pain relief?
Answer: NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen are typically considered the best options for quick and effective relief due to their anti-inflammatory effects. However, in severe cases, prescription corticosteroids or neuropathic pain medications may be necessary.
2. Are there any over-the-counter sciatica medication options?
Answer: Yes, NSAIDs and acetaminophen are readily available over-the-counter options that can help manage mild to moderate sciatica pain. Topical analgesics are also accessible for localized relief.
3. How long should I take sciatica medication?
Answer: The duration depends on the severity of symptoms and response to treatment. Short-term use is generally recommended for acute pain, while longer durations require medical oversight to prevent side effects.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Sciatica Pain
Finding effective sciatica medication options to relieve pain quickly can significantly improve your daily comfort and mobility. While medications like NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and neuropathic agents are powerful tools in pain management, they work best when integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate medication and dosage tailored to your specific condition.
Don’t let sciatica pain control your life—take proactive steps today by seeking professional guidance and exploring the most effective medication options. Your swift relief and recovery are within reach!
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication or treatment plan.